[ARM Linux 驱动开发] 设备树下的 LED 驱动
这篇文章我们介绍如何在利用设备树编写 LED 驱动。这节的内容不是很复杂,可以说是之前两篇文章:[ARM Linux 驱动开发] “新”字符设备驱动、[ARM Linux 驱动开发] linux 设备树 的结合版本。
借此机会我们正好巩固一下如何自动分配设备号和注册设备、如何自动创建设备文件、如何获取设备树数据。
修改设备树文件
我们之前进行 linux 系统移植的时候,使用的设备树文件是 arch/arm/boot/dts/imx6ull-my-emmc.dts。因此,我们现在对它进行修改,在根节点的末尾添加自己 led 节点:
- / {
- /* ………… */
- hanhanled {
- #address-cells = <1>;
- #size-cells = <1>;
- compatible = "hanhan-led";
- status = "okay";
- reg = <0x020c406c 0x04
- 0x020e0068 0x04
- 0x020e02f4 0x04
- 0x0209c004 0x04
- 0x0209c000 0x04>;
- };
- };
开发板教程中的这个 #address-cells 和 #size-cells 应该是有的问题,因为它们只是针对当前节点的子节点。
但也不影响我们后续驱动程序的编写,因为后续编写的驱动程序中压根没有利用到这个属性😂。(但后续还是要注意)
本着之前所说的“用到再看”的原则,下面抄录一下自定义节点中用到的属性说明:
#address-cells 和 #size-cells 1
属性名称:#address-cells,#size-cells
值类型:<u32>
描述:
#address-cells 和 #size-cells 属性可用于设备树层次结构中有子节点的任何设备节点,并描述子设备节点应该如何寻址。#address-cells 属性定义了 <u32> 单元格的数量,其用于对子节点 reg 属性中的地址字段进行编码。#size-cells 属性定义了 <u32> 单元格的数量,其用于对子节点 reg 属性中的大小字段进行编码。
#address-cells 和 #size-cells 属性不继承于设备树的祖先节点。应该明确定义它们。
一个设备树标准兼容的引导程序需要在所有有孩子的节点上提供 #address-cells 和 #size-cells。
如果这些属性丢失,则客户端程序应假定 #address-cells 的默认值为 2,#size-cells 的默认值为 1。
样例:
- soc {
- #address-cells = <1>;
- #size-cells = <1>;
- serial@4600 {
- compatible = "ns16550";
- reg = <0x4600 0x100>;
- clock-frequency = <0>;
- interrupts = <0xA 0x8>;
- interrupt-parent = <&ipic>;
- };
- };
在这个样例中,soc 节点的 #address-cells 和 #size-cells 属性都设置为 1。这个设置指定,该节点的所有孩子节点需要一个单元格来表示地址,且一个单元格来表示大小。
这个串行设备的 reg 属性必须遵循其父节点(soc)中设置的此规范——地址由一个单元格表示(0x4600),大小由一个单元格表示(0x100)。
reg 2
属性名称:reg
值类型:<prop-encoded-array> 编码为任意数量的(地址,长度)对。
描述:
reg 属性描述设备资源的地址,其所在地址空间由其父总线定义。最常见的是指内存映射 IO 寄存器块的偏移量和长度,但在某些总线类型上可能有不同的含义。根节点所定义的地址空间中的地址是 CPU 真实地址。
reg 该值是一个 <prop-encoded-array>,由任意数量的地址和长度对组成,<地址,长度>。指定地址和长度所需的 <u32> 单元数量是特定于总线的,由设备节点的父节点中 #address-cells 和 #size-cells 属性指定。如果父节点指定 #size-cells 为值 0,则 reg 值中的长度字段将被省略。
样例:
假设片上系统中的一个器件有两个寄存器块:SOC 中偏移 0x3000 处的 32 字节块和偏移量 0xFE00 处的 256 字节块。reg 属性的编码如下(假设 #address-cells 和 #size-cells 的值为 1):
- reg = <0x3000 0x20 0xFE00 0x100>;
compatible 3
属性名称:compatible
值类型:<stringlist>。
描述:
compatible 属性值由一个或多个字符串组成,其定义设备特定编程模型。客户端程序应使用这个字符串列表来选择设备驱动程序。属性值由 null 结尾的字符串的串联列表组成,从最具体到最一般。它们允许一个设备表达其与一系列类似设备的兼容性,潜在地允许单个设备驱动程序匹配多个设备。
推荐的格式是制造商,型号,其中制造商是描述制造商名称的字符串(如股票代码符号),型号指定模型编号。
样例:
- compatible = "fsl,mpc8641", "ns16550";
在本例中,操作系统将首先尝试定位支持 fsl,mpc8641 的设备驱动程序。如果未找到驱动程序,则尝试定位支持更通用的 ns16550 设备类型的驱动程序。
以上内容再“白话”的总结一下。#address-cells、#size-cells 和 reg 属性是一组的,reg 中可以定义任意对(地址,长度)对,而地址字段的大小由 #address-cells 指定,大小字段的大小由 #size-cells 指定。compatible 属性定义设备的兼容性信息,有点类似 html 里的字体匹配,前面定义的匹配不上就匹配后面的。status 属性上面介绍中没有给出,但看名字也容易理解,用作指明设备的状态。
修改好设备树文件之后,使用
- > make dtbs ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf-
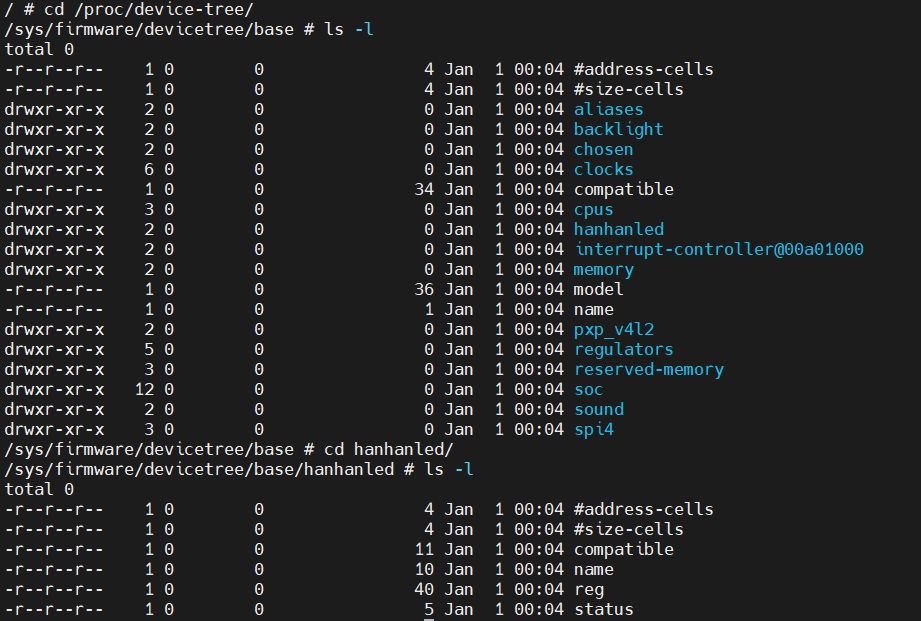
命令进行编译,会产生想要的 arch/arm/boot/dts/imx6ull-my-emmc.dtb 文件。将其放在服务器上,然后重启开发板来重新引导。如图 1 所示,我们可以通过查看 /proc/device-tree/ 目录,来检查新添加的节点是否添加成功。
1 《Devicetree specification》 : 2.3.5 #address-cells and #size-cells
2 《Devicetree specification》 : 2.3.6 reg
3 《Devicetree specification》 : 2.3.1 compatible
驱动编写
修改好设备树文件之后,我们就可以开始编写驱动设备了。总体框架和 [ARM Linux 驱动开发] “新”字符设备驱动 中的一样:自动分配设备号、自动创建设备文件。设备树操作函数和 [ARM Linux 驱动开发] linux 设备树 中的一样。
- #include <linux/module.h>
- #include <linux/cdev.h>
- #include <linux/device.h>
- #include <linux/fs.h>
- #include <asm/io.h>
- #include <asm/uaccess.h>
- #include <linux/of.h>
- #include <linux/slab.h>
- #include <linux/of_address.h>
- #define LED_CNT 1
- #define LED_NAME "dtsled"
- void __iomem* CCM_CCGR1;
- void __iomem* SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03;
- void __iomem* SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03;
- void __iomem* GPIO1_GDIR;
- void __iomem* GPIO1_DR;
- struct LedDev
- {
- /* 设备号相关 */
- dev_t devId;
- int major;
- int minor;
- /* cdev */
- struct cdev cdev;
- /* mdev */
- struct class* class;
- struct device* device;
- };
- struct LedDev ledDev;
- int led_open(struct inode* indoe, struct file* filp)
- {
- printk("led_open\n");
- return 0;
- }
- int led_release(struct inode* indoe, struct file* filp)
- {
- printk("led_release\n");
- return 0;
- }
- void turn_on_led(void)
- {
- int val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
- val &= ~(1 << 3);
- writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
- }
- void turn_off_led(void)
- {
- int val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
- val |= 1 << 3;
- writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
- }
- ssize_t led_write(struct file* file, const char __user* buf, size_t count, loff_t* ppos)
- {
- int res;
- char status;
- res = copy_from_user(&status, buf, sizeof(status));
- if (res < 0)
- {
- printk("copy_from_user error\n");
- return -EFAULT;
- }
- if (status == 1)
- turn_on_led();
- else
- turn_off_led();
- return 0;
- }
- const struct file_operations led_fops =
- {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .open = led_open,
- .release = led_release,
- .write = led_write,
- };
- static int led_init(void)
- {
- /* 获取设备树数据 */
- int res, i, val;
- const char* str;
- u32 regData[10];
- struct device_node* nd = of_find_node_by_path("/hanhanled");
- if (nd == NULL)
- {
- printk("/hanhanled node find failed\n");
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- // compatible
- res = of_property_read_string(nd, "compatible", &str);
- if (res >= 0)
- {
- printk("compatible = %s\n", str);
- }
- // status
- res = of_property_read_string(nd, "status", &str);
- if (res >= 0)
- {
- printk("status = %s\n", str);
- }
- // reg
- res = of_property_read_u32_array(nd, "reg", regData, 10);
- if (res >= 0)
- {
- for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
- {
- printk("%d ", regData[i]);
- }
- printk("\n");
- }
- /* 寄存器映射 */
- CCM_CCGR1 = ioremap(regData[0], regData[1]);
- SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(regData[2], regData[3]);
- SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(regData[4], regData[5]);
- GPIO1_GDIR = ioremap(regData[6], regData[7]);
- GPIO1_DR = ioremap(regData[8], regData[9]);
- // 使能 GPIO1 时钟
- val = readl(CCM_CCGR1);
- val |= (3 << 26);
- writel(val, CCM_CCGR1);
- // 复用为 GPIO
- writel(5, SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03);
- // IO 属性
- writel(0x10b0, SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03);
- // GPIO 设置为输出
- val = readl(GPIO1_GDIR);
- val |= (1 << 3);
- writel(val, GPIO1_GDIR);
- // led 默认关闭
- val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
- val |= (1 << 3);
- writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
- /* 注册设备号 */
- if (ledDev.major)
- {
- ledDev.devId = MKDEV(ledDev.major, ledDev.minor);
- register_chrdev_region(ledDev.devId, LED_CNT, LED_NAME);
- }
- else
- {
- alloc_chrdev_region(&ledDev.devId, 0, LED_CNT, LED_NAME);
- ledDev.major = MAJOR(ledDev.devId);
- ledDev.minor = MINOR(ledDev.devId);
- }
- printk("major = %d, minor = %d\n", ledDev.major, ledDev.minor);
- /* 设置 cdev */
- ledDev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
- cdev_init(&ledDev.cdev, &led_fops);
- cdev_add(&ledDev.cdev, ledDev.devId, LED_CNT);
- /* 设置 mdev */
- ledDev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, LED_NAME);
- if (IS_ERR(ledDev.class))
- {
- return PTR_ERR(ledDev.class);
- }
- ledDev.device = device_create(ledDev.class, NULL, ledDev.devId, NULL, LED_NAME);
- if (IS_ERR(ledDev.device))
- {
- return PTR_ERR(ledDev.device);
- }
- return 0;
- }
- static void __exit led_exit(void)
- {
- cdev_del(&ledDev.cdev);
- unregister_chrdev_region(ledDev.devId, LED_CNT);
- device_destroy(ledDev.class, ledDev.devId);
- class_destroy(ledDev.class);
- }
- module_init(led_init);
- module_exit(led_exit);
- MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- MODULE_AUTHOR("hanhan");
这边主要关注设备树数据读取的部分。代码中第 101 至 112 行,分别只是“象征性”地读取了 compatible 和 status 属性,并没有真正用到它们。第 114 至 122 行按数组形式读取了 reg 属性,然后在 125 至 129 行按照 (地址,长度) 对,使用 ioremap 函数进行寄存器映射。这边我们可以看到,就是原来寄存器地址的硬编码从代码中变到了设备树文件中,是那股“设计模式”的味道。
获取 reg 属性的内容再用 ioremap 函数进行映射的操作,可以直接用 of_iomap 函数进行替代,更加方便。对应内容为下述代码中的 132 至 136 行。
- #include <linux/module.h>
- #include <linux/cdev.h>
- #include <linux/device.h>
- #include <linux/fs.h>
- #include <asm/io.h>
- #include <asm/uaccess.h>
- #include <linux/of.h>
- #include <linux/slab.h>
- #include <linux/of_address.h>
- #define LED_CNT 1
- #define LED_NAME "dtsled"
- void __iomem* CCM_CCGR1;
- void __iomem* SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03;
- void __iomem* SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03;
- void __iomem* GPIO1_GDIR;
- void __iomem* GPIO1_DR;
- struct LedDev
- {
- /* 设备号相关 */
- dev_t devId;
- int major;
- int minor;
- /* cdev */
- struct cdev cdev;
- /* mdev */
- struct class* class;
- struct device* device;
- };
- struct LedDev ledDev;
- int led_open(struct inode* indoe, struct file* filp)
- {
- printk("led_open\n");
- return 0;
- }
- int led_release(struct inode* indoe, struct file* filp)
- {
- printk("led_release\n");
- return 0;
- }
- void turn_on_led(void)
- {
- int val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
- val &= ~(1 << 3);
- writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
- }
- void turn_off_led(void)
- {
- int val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
- val |= 1 << 3;
- writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
- }
- ssize_t led_write(struct file* file, const char __user* buf, size_t count, loff_t* ppos)
- {
- int res;
- char status;
- res = copy_from_user(&status, buf, sizeof(status));
- if (res < 0)
- {
- printk("copy_from_user error\n");
- return -EFAULT;
- }
- if (status == 1)
- turn_on_led();
- else
- turn_off_led();
- return 0;
- }
- const struct file_operations led_fops =
- {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .open = led_open,
- .release = led_release,
- .write = led_write,
- };
- static int led_init(void)
- {
- /* 获取设备树数据 */
- int res, i, val;
- const char* str;
- u32 regData[10];
- struct device_node* nd = of_find_node_by_path("/hanhanled");
- if (nd == NULL)
- {
- printk("/hanhanled node find failed\n");
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- // compatible
- res = of_property_read_string(nd, "compatible", &str);
- if (res >= 0)
- {
- printk("compatible = %s\n", str);
- }
- // status
- res = of_property_read_string(nd, "status", &str);
- if (res >= 0)
- {
- printk("status = %s\n", str);
- }
- // reg
- res = of_property_read_u32_array(nd, "reg", regData, 10);
- if (res >= 0)
- {
- for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
- {
- printk("%d ", regData[i]);
- }
- printk("\n");
- }
- /* 寄存器映射 */
- #if 0
- CCM_CCGR1 = ioremap(regData[0], regData[1]);
- SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(regData[2], regData[3]);
- SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(regData[4], regData[5]);
- GPIO1_GDIR = ioremap(regData[6], regData[7]);
- GPIO1_DR = ioremap(regData[8], regData[9]);
- #else
- CCM_CCGR1 = of_iomap(nd, 0);
- SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03 = of_iomap(nd, 1);
- SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03 = of_iomap(nd, 2);
- GPIO1_GDIR = of_iomap(nd, 3);
- GPIO1_DR = of_iomap(nd, 4);
- #endif
- // 使能 GPIO1 时钟
- val = readl(CCM_CCGR1);
- val |= (3 << 26);
- writel(val, CCM_CCGR1);
- // 复用为 GPIO
- writel(5, SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03);
- // IO 属性
- writel(0x10b0, SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03);
- // GPIO 设置为输出
- val = readl(GPIO1_GDIR);
- val |= (1 << 3);
- writel(val, GPIO1_GDIR);
- // led 默认关闭
- val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
- val |= (1 << 3);
- writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
- /* 注册设备号 */
- if (ledDev.major)
- {
- ledDev.devId = MKDEV(ledDev.major, ledDev.minor);
- register_chrdev_region(ledDev.devId, LED_CNT, LED_NAME);
- }
- else
- {
- alloc_chrdev_region(&ledDev.devId, 0, LED_CNT, LED_NAME);
- ledDev.major = MAJOR(ledDev.devId);
- ledDev.minor = MINOR(ledDev.devId);
- }
- printk("major = %d, minor = %d\n", ledDev.major, ledDev.minor);
- /* 设置 cdev */
- ledDev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
- cdev_init(&ledDev.cdev, &led_fops);
- cdev_add(&ledDev.cdev, ledDev.devId, LED_CNT);
- /* 设置 mdev */
- ledDev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, LED_NAME);
- if (IS_ERR(ledDev.class))
- {
- return PTR_ERR(ledDev.class);
- }
- ledDev.device = device_create(ledDev.class, NULL, ledDev.devId, NULL, LED_NAME);
- if (IS_ERR(ledDev.device))
- {
- return PTR_ERR(ledDev.device);
- }
- return 0;
- }
- static void __exit led_exit(void)
- {
- cdev_del(&ledDev.cdev);
- unregister_chrdev_region(ledDev.devId, LED_CNT);
- device_destroy(ledDev.class, ledDev.devId);
- class_destroy(ledDev.class);
- }
- module_init(led_init);
- module_exit(led_exit);
- MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- MODULE_AUTHOR("hanhan");
